In figure , assuming the diodes to be ideal ,
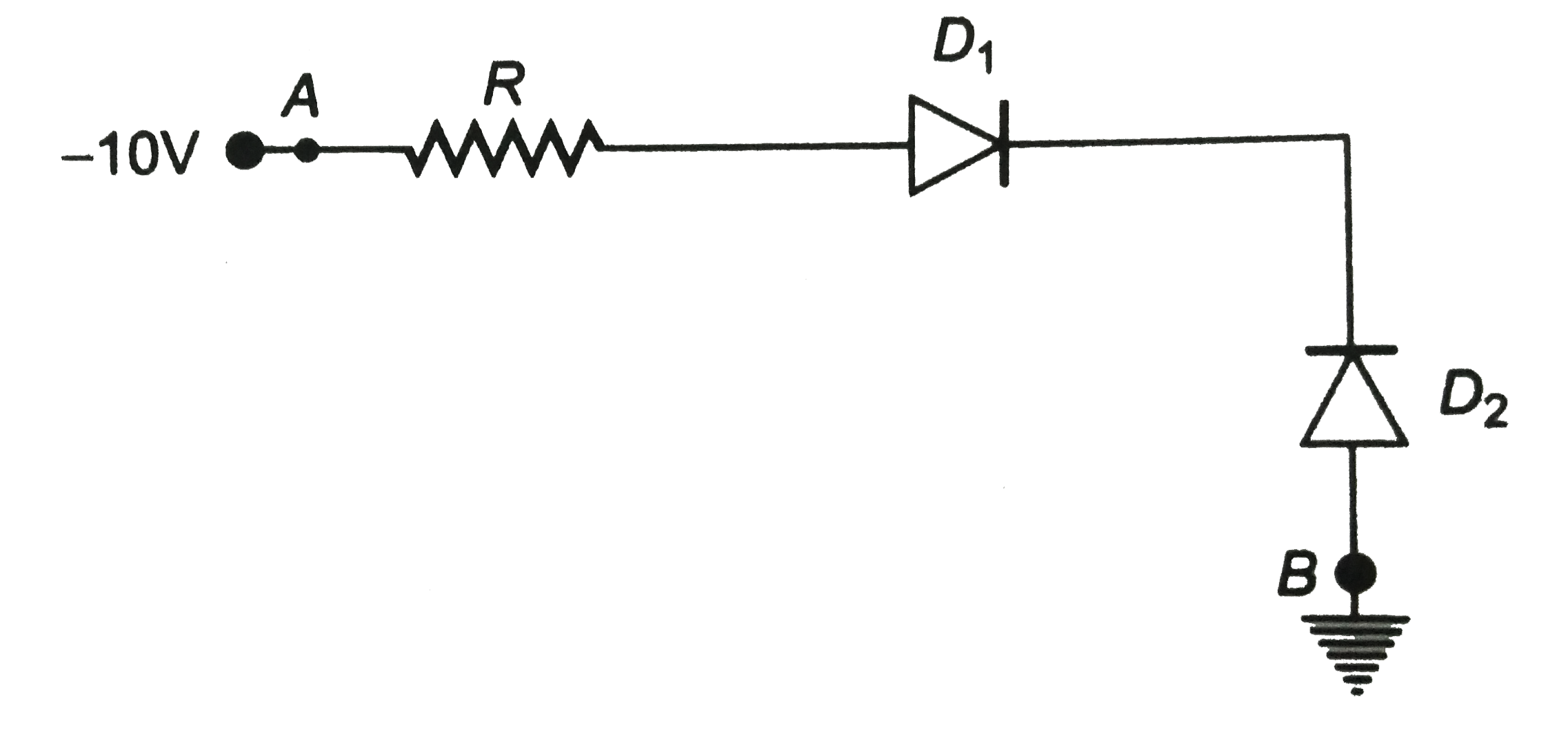
A. `D_(1)` is forward biased and `D_(2)` is reverse biased and hence current flows from `A` to `B`
B. `D_(2)` is forward biased and `D_(1)` is reverse biased and hence no current flows from `B` to `A` and vice versa
C. `D_(1)` and `D_(2)` are both forward biased and hence current flows form `A` to `B`
D. `D_(1)` and `D_(2)` are both revrese biased and hence no current flows from `A` and `B` and vica-versa.

A. `D_(1)` is forward biased and `D_(2)` is reverse biased and hence current flows from `A` to `B`
B. `D_(2)` is forward biased and `D_(1)` is reverse biased and hence no current flows from `B` to `A` and vice versa
C. `D_(1)` and `D_(2)` are both forward biased and hence current flows form `A` to `B`
D. `D_(1)` and `D_(2)` are both revrese biased and hence no current flows from `A` and `B` and vica-versa.

Correct Answer – B
In the given circuit p-side of `p-n` function `D_(1)` is connected to lower voltage and n-side of `D_(1)` to higher voltage. Thus `D` is reverse biased. The p-side of `p-n` junction `D_(2)` is lower potential.
Therefore `D_(2)` is forward biased.
Hence, current flows through the junction `B` to `A`.